Computers store characters as a series of 0’s and 1’s. But there are different ways of translating characters into bits. These translations are called file encodings. When the software you use to open a file assumes a file is using one encoding but the file is actually using a different encoding, you get garbled text and data.
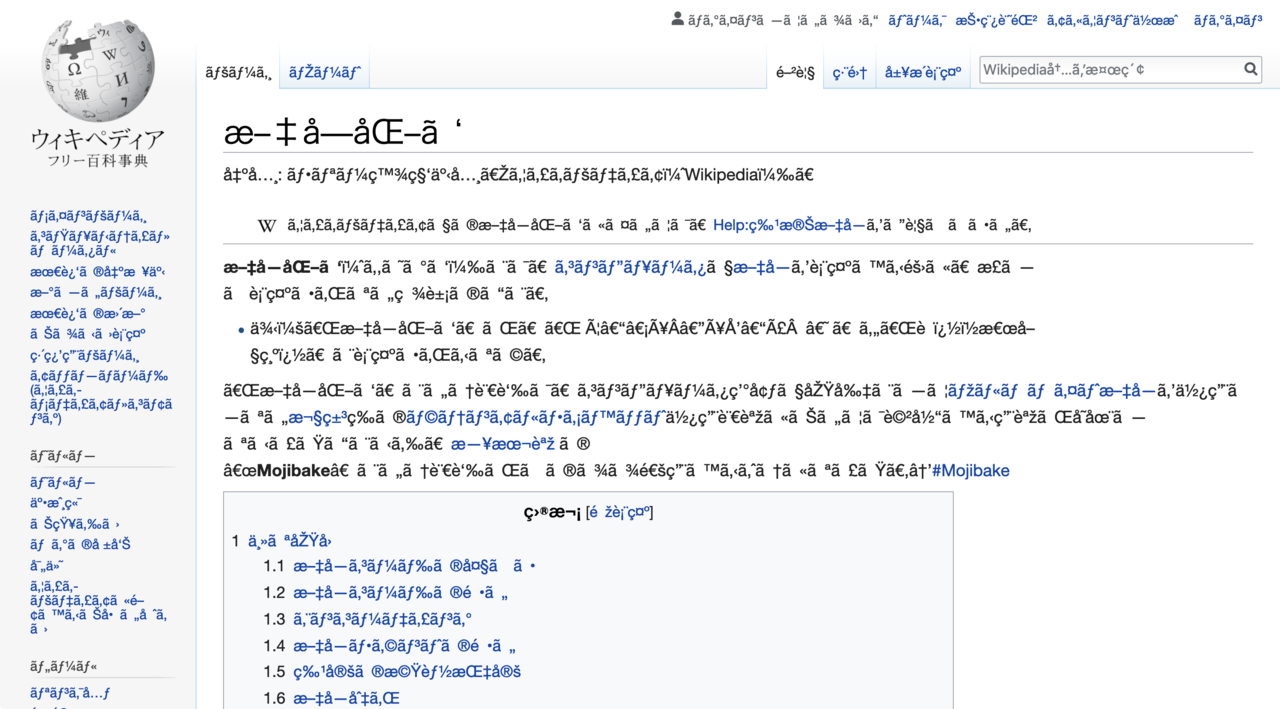
A Wikipedia article in UTF-8 encoding displayed using the Windows-1252 encoding. Source: Wikimedia Foundation, CC BY SA 3.0
Some encodings lack encodings for special characters, like letters with specific accents. When these letters are displayed through one of these encodings, the characters with accents will be replaced by weird symbols or with the generic “�” symbol. This is a sign the wrong encoding is used to read and display a file.
Many software programs offer the option to set the encoding both when saving a file and when opening or importing a file. The UTF-8 encoding is a widely used encoding and a safe bet as a default.
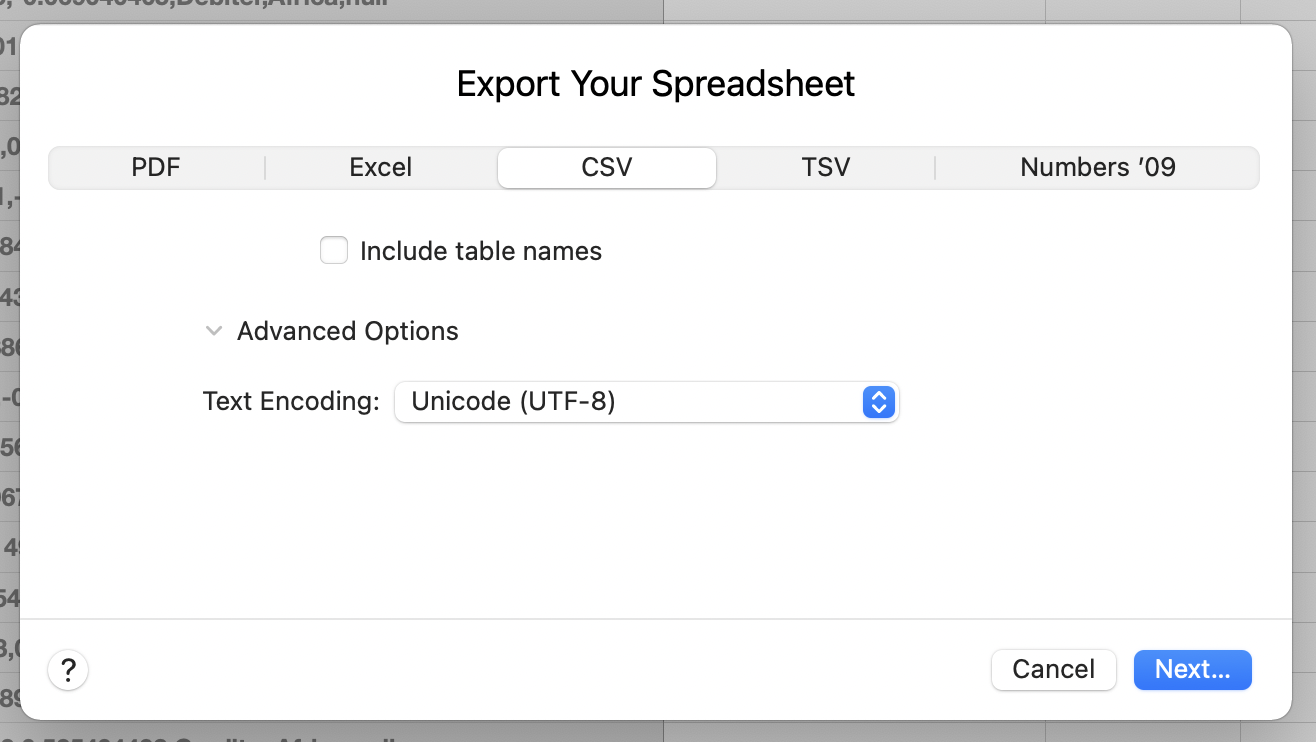
Setting the file encoding in Mac OS Numbers. Source: Maarten Lambrechts, CC BY SA 4.0
If you notice file encoding issues in your data, you should ask your data provider what encoding the data file is using.