When you click a link and your web browser navigates to a new page, a lot of things happen behind the scenes. In order to understand how HTML is involved in all this, you should have an understanding of these processes.
In its most basic form, when a web browser opens a page, it is sending a request to a web server to send the content of the requested page. If the request is valid, the web server will respond by sending the content of the page to the browser, after which the browser can display it. In its most basic form, that content is described in a HTML file.
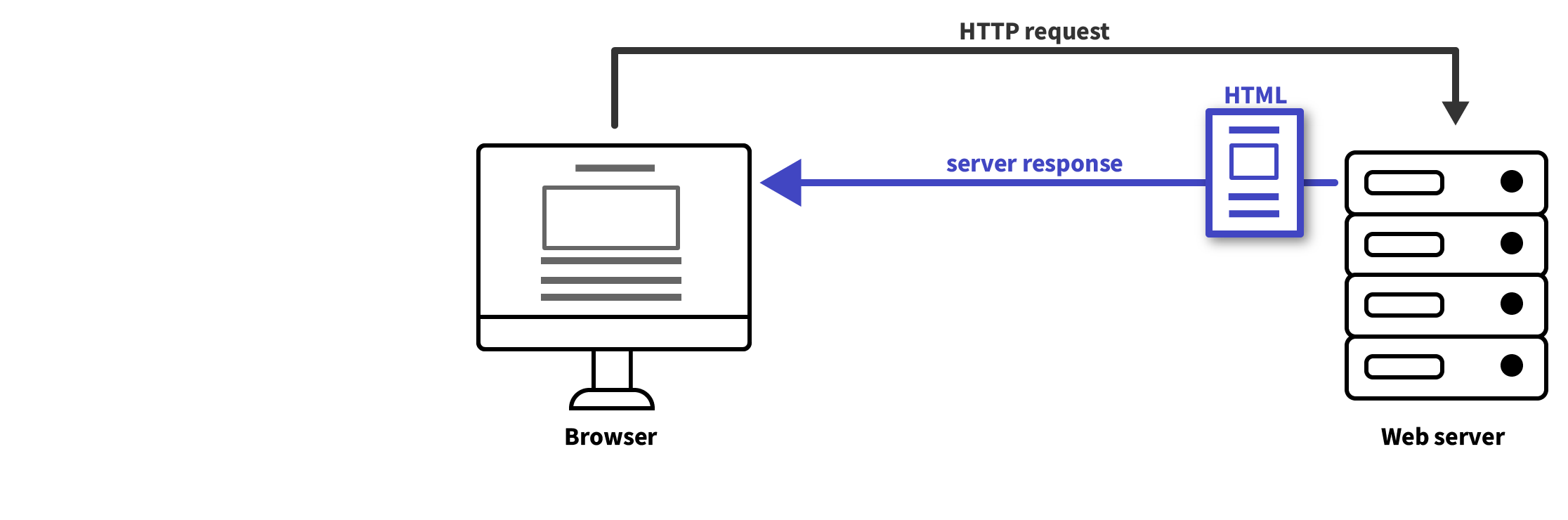
Source: Maarten Lambrechts, CC BY SA 4.0
HTML is is human readable: you can open a HTML file with any text editor, like Notepad on Windows or TextEdit on Mac, and you will be able to read and understand its content without much difficulties. HTML is also machine readable: after a browser has received the HTML of a web page, it parses it and renders the content on screen.